Introduction
In today’s digital era, cyber threats and cyber-attack continue to evolve. Social engineering attacks is one of the most prevalent and dangerous tactics used by cybercriminals in recent years.
But what exactly is social engineering? It refers to the manipulation of individuals into divulging sensitive data, confidential information, clicking malicious links, or even granting unauthorized access to systems. Unlike traditional hacking, which focuses on breaching technical defenses, ransomware, it exploits human psychology to achieve its goals.
In this blog you will be getting a 360-degree view of socialengineering meaning, types, stages, current cyber-attack trends and prevention strategies.
What is Social Engineering?
Socialengineering attacks manipulate individuals into sharing sensitive information, downloading malware, or making financial transactions under false pretenses. These attacks often lead to identity theft, financial loss, and organizational data breaches.
Cybercriminals use socialengineering to obtain personal details like login credentials, credit card numbers, and bank account information. Once data received, this data can be used for fraudulent activities, including unauthorized purchases and large-scale cyberattacks, such as deploying ransomware within corporate networks.
How Does Social Engineering Work?
Socialengineering is effective because it exploits fundamental aspects of human behavior. Attackers manipulate victims using psychological tactics that make them act against their best interests. Common techniques for cyber-attacks include:
- Impersonation of Trusted Brands: Attackers create fake websites or emails that resemble legitimate businesses, tricking victims into revealing credentials.
- Exploiting Curiosity and Helpfulness: Fraudsters may pose as IT personnel offering assistance or as social media contacts seeking engagement.
- Greed-Based Attacks: Scams like the classic “Nigerian Prince” fraud promise financial rewards in exchange for personal details.
- Authority Exploitation: Scammers pose as government officials, law enforcement, or company executives to manipulate victims.
- Creating Fear or Urgency: Victims are led to believe they must act immediately—such as fixing a banking issue or responding to a cyber threat.
Why is Social Engineering Dangerous?
Socialengineering attacks are particularly dangerous because they bypass traditional cybersecurity measures. Even organizations with strong firewalls, encryption, and types of application security are vulnerable if an attacker manipulates an employee.
Consequences of social engineering in cyber security attacks include:
- Identity theft
- Unauthorized financial transactions
- Damage to personal or corporate reputation
- Data breaches and loss of confidential information
- Installation of malware, including ransomware
According to recent Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM, breaches caused by socialengineering tactics are among the costliest, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures such as multi-factor authentication.
The Social Engineering Lifecycle
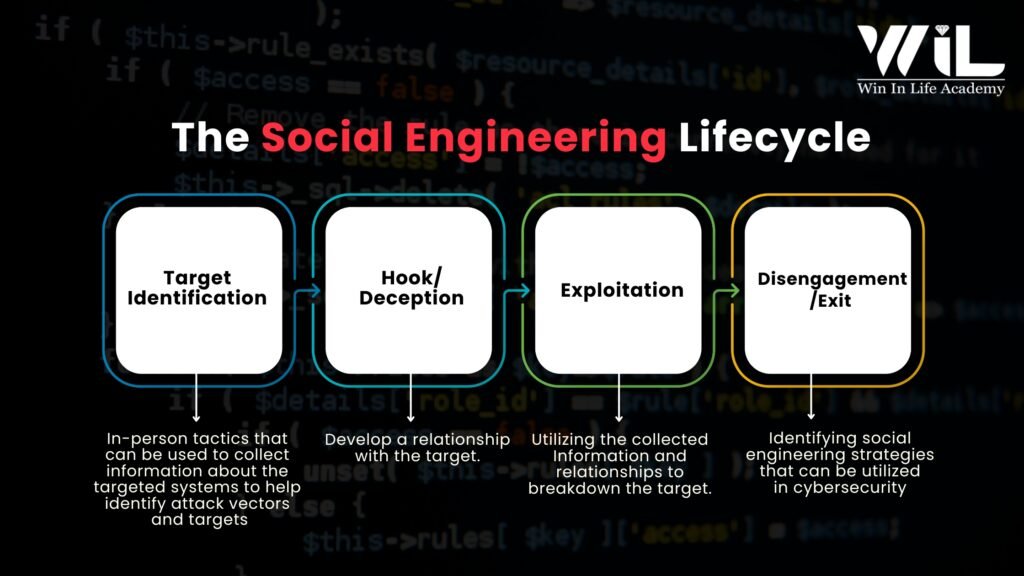
Socialengineering in cyber security attacks typically follow a structured process involving four key stages:
- Target Identification: The attacker gathers background information on potential victims to determine vulnerabilities. This phase involves reconnaissance, where attackers research their targets using publicly available data, social media, or corporate websites to identify weak points.
- Hook/Deception: The attacker initiates contact with the target, gaining their trust through deceptive tactics. This could be via email, phone calls, or even in-person interactions. By masquerading as a legitimate entity or authority, they manipulate the victim into a false sense of security.
- Exploitation: Once trust is established, the attacker leverages the victim’s weaknesses to extract sensitive information. This could involve asking for login credentials, tricking them into downloading malware, or persuading them to perform unauthorized actions like transferring money or granting access to restricted areas.
- Disengagement/Exit: After achieving their objective, the attacker ends communication and covers their tracks. This ensures the victim remains unaware of the breach for as long as possible, allowing the attacker to use the stolen information before detection.
Types of Social Engineering Attacks
Socialengineering attacks come in various forms, each exploiting human psychology in different ways:
- Phishing: This is one of the most common forms of socialengineering in cyber security attacks. It involves sending fraudulent emails or text messages that appear to come from trusted sources. These messages create a sense of urgency, prompting victims to click on malicious links or provide sensitive information like passwords and credit card details.
- Spear Phishing: Unlike general phishing, spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations. Attackers research their victims and craft personalized messages that appear more convincing. This makes spear phishing attacks much harder to detect and more successful in stealing sensitive data.
- Baiting: Baiting attacks exploit human curiosity or greed by offering something enticing, such as free software or job opportunities. For example, attackers may leave malware-infected USB drives in public places, hoping victims will plug them into their computers.
- Scareware: Scareware tricks victims into believing their system is infected with malware, prompting them to download fake antivirus software. These fake security tools often contain actual malware that compromises the victim’s system.
- Pretexting: In pretexting attacks, scammers create a false scenario to trick victims into providing sensitive information. They may pose as a company’s IT support staff, asking for login credentials to “fix” an issue, or as a bank representative verifying account detail.
- Tailgating (Piggybacking): This involves an attacker gaining physical access to restricted areas by following authorized personnel. For example, an attacker may pretend to have forgotten their security badge and ask an employee to hold the door open for them.
- Phone-Based Attacks (Vishing): In this type of attack, scammers call victims while posing as customer support representatives, bank officials, or IT personnel. They use socialengineering tactics to extract personal information, login credentials, or financial details from their targets.
Each of these attacks relies on manipulating trust, urgency, or authority to deceive victims. Being aware of these tactics and implementing security measures like multi-factor authentication can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to socialengineering in cyber security attacks.
Enroll now: Certified Ethical Hacker Course
Latest Social Engineering Attacks
In recent years, several notable social engineering attacks have highlighted the evolving tactics of cybercriminals, few of them are mentioned bellow:
- 2020 Twitter Bitcoin Scam: Cybercriminals compromised Twitter’s internal systems through targeted social engineering in cyber security attacks on employees. They hijacked high-profile accounts, including those of Barack Obama and Apple, to promote a cryptocurrency scam, amassing over $100,000 in Bitcoin.
- 2022 Uber Breach: An 18-year-old hacker used socialengineering to obtain an Uber employee’s credentials, gaining access to internal systems and posting explicit content on the company’s Slack platform. mitnicksecurity.com
- 2022 Rockstar Games Hack: The same hacker infiltrated Rockstar Games’ internal Slack channel, accessing and leaking source code for the unreleased “Grand Theft Auto” sequel. mitnicksecurity.com
- 2024 Deepfake Impersonation: A deepfake video call impersonating Ukraine’s former foreign minister nearly deceived U.S. Senator Ben Cardin, highlighting the sophistication of modern socialengineering tactics. theverge.com
- 2024 Iranian Hackers Indicted: Three Iranian nationals were charged with hacking email accounts associated with Donald Trump’s presidential campaign, aiming to influence the election by sharing confidential materials. Politico
These incidents underscore the critical need for heightened vigilance and robust security measures to counter increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. That is why in today’s era learning cyber security and ethical hacking is a priority for freshers and experienced professionals.
Enroll now: Cybersecurity Courses
How to Identify and Prevent Social Engineering Attacks

1. Red Team Assessments
Organizations conduct red team assessments to simulate real-world socialengineering in cyber security attacks. These assessments reveal security weaknesses and provide actionable recommendations.
2. Security Awareness Training
One of the most effective defenses against socialengineering attacks is educating employees. Training should focus on:
- Recognizing phishing emails
- Verifying unexpected requests
- Avoiding suspicious links or downloads
- Implementing security best practices such as multi-factor authentication
3. Secure Architecture
Designing systems with security in mind ensures that even if one component is compromised, damage remains limited. Security controls should include:
- Network segmentation
- Regular software updates
- Role-based access control
Conclusion
Socialengineering remains one of the most effective tactics used by cybercriminals. By exploiting human psychology, attackers bypass traditional cybersecurity measures and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Organizations and individuals must stay vigilant, implement multi-factor authentication, and invest in robust security training to mitigate these risks.
As the threat landscape evolves, understanding socialengineering in cyber security and adopting proactive security measures will be essential in safeguarding personal and corporate data from cybercriminals.
As protecting our digital world is important now a day, if you are ready to take your cybersecurity career and skills to the next level? Explore Win In Life’s structured curriculum and comprehensive training at Win in Life Academy and embark on your journey to become a cybersecurity expert with us Cyber security course.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is social engineering meaning?
A: Socialengineering refers to psychological manipulation of human behavior into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. It often exploits human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to system information, data, or networks.
Q: How can multi factor authentication prevent ransomware attacks?
A: MFA enhances security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password, a security token, or biometric authentication. Even if cyber attackers obtain login credentials through socialengineering, MFA adds an extra layer of defense, making unauthorized access more difficult.
Q: What are the common types of socialengineering attacks?
A: Some of the most common socialengineering attacks include Phishing, Pretexting, Baiting, and Tailgating.
Q: What role does application security play in preventing cyber threats and what are the types of application security?
A: Application security includes various measures designed to protect software and systems from cyber threats. The types of application security that help prevent cyber-attacks include:
- Authentication security – Using strong passwords and MFA to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access control – Restricting user permissions based on roles.
- Data encryption – Protecting sensitive data from interception or theft.
- Security awareness training – Educating employees on recognizing social engineering tactics.
Q: How can individuals and organizations protect themselves from cyber-attacks?
A: To reduce the risk of cyber-attacks, following are the best practices:
- One need to be very cautious of unsolicited emails, calls, or messages requesting sensitive information.
- Use multi-factor authentication for all types of accounts.
- Double check and verify requests for sensitive data through official communication channels.
- Educate employees about different types of cyber-attacks.
- Implement strong application security measures to safeguard digital assets of the organization.
Reference:
- Anderson, Ross J. (2008). Security engineering: a guide to building dependable distributed systems (2 ed.). Indianapolis, IN: Wiley. p. 1040. ISBN 978-0-470-06852-6. Chapter 2, page 17
- “Social Engineering Defined”. Security Through Education. Retrieved 3 October 2021.
- Salahdine, Fatima (2019). “Social Engineering Attacks: A Survey”. School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of North Dakota. 11 (4): 89.





